What is Heat Sink and its importance?
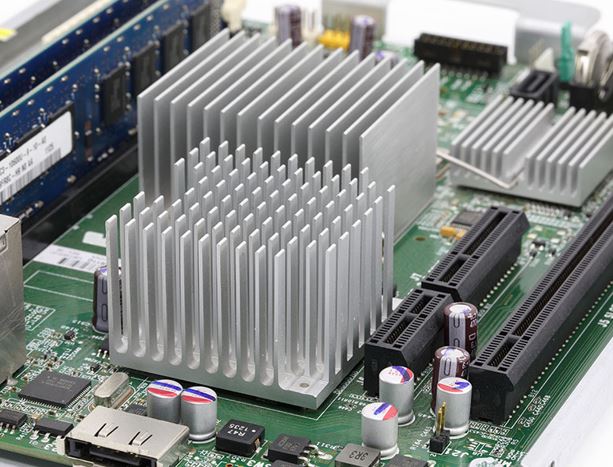

Every electrical and electronic component in a circuit generates some amount of heat while the circuit is executed by providing power supply. Typically high-power semiconducting devices like power transistors and optoelectronics such as light-emitting diodes, lasers generate heat in considerable amounts and these components are inadequate to dissipate heat, as their dissipation capability is significantly low.
Due to this, heating up of the components leads to premature failure and may cause the failure of the entire circuit or system’s performance. So, to conquer these negative aspects, heat sinks must be provided for cooling purposes.
What is a Heat Sink?
A heat sink is an electronic component or a device of an electronic circuit which disperses heat other components (mainly the power transistors) of a circuit into the surrounding medium and cools them for improving their performance, reliability and also avoids the premature failure of the components. For the cooling purpose, it incorporates a fan or cooling device.
Heat Sink Principle
Fourier’s law of heat conduction states that if the temperature gradient is present in a body, then the heat will transfer a high-temperature region to allow- temperature region. And, this can be achieved in three different ways, such as convection, radiation and conduction.
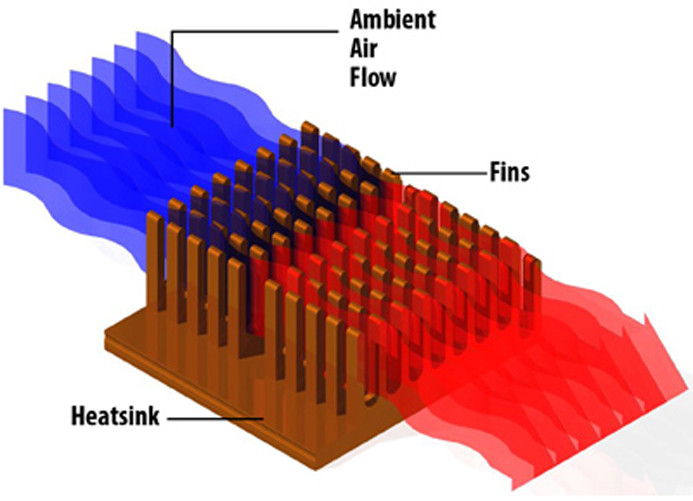
Whenever two objects with different temperatures come in contact with each other, conduction occurs causing the fast-moving molecules of the high-heat object to collide with the slow-moving molecules of the cooler objects, and thus, transfers thermal energy to the cooler object, and this is termed as thermal conductivity.
Similarly, heat sink transfers the heat or thermal energy a high-temperature component to a low-temperature medium like air, water, oil, etc. Usually, the air is used as a low-temperature medium; and, if the water is used as a medium, then it is termed as the cold plate.
Aluminum Heat Sink
Heat sinks are generally made of metals, and aluminum is the most common metal used in heat sink. We are aware of the fact that the thermal conductivity of each metal is different. The thermal conductivity of metal is proportional to the heat transfer in heat sink. Thus, if the thermal conductivity of the metal increases, then the heat transferring capacity of the heat sink will also increase.
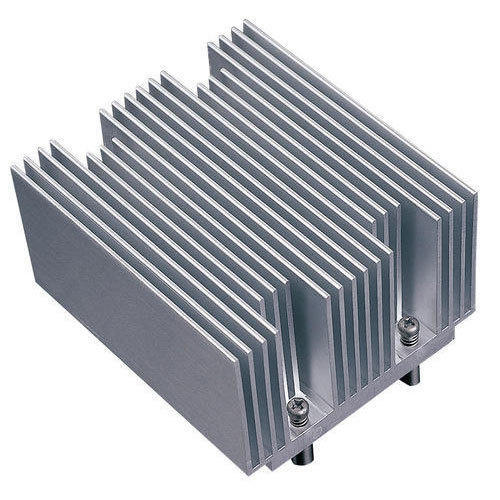

The thermal conductivity of the aluminum is 235 W/mK, it is the cheapest and lightweight metal. Aluminum heat sinks are also called as extruded heat sinks as they can be made using extrusion.
KIMSEN is proud to bring high quality aluminum extrusion, components & modules which meet international standards.
For specific advice, please contact Hotline 0243 795 7410 or email info@kimsen.vn
KIMSEN INDUSTRIAL CORPORATION
Head Office & Factory: Yen Phong Industrial Park, Yen Phong Dist., Bac Ninh Pro., Vietnam
Hanoi Office: 14th floor, TTC Tower, No. 19 Duy Tan Str., Cau Giay Dist., Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline: 0243 795 7410
Email: info@kimsen.vn
Images source: Internet
*Reference: https://www.elprocus.com/different-types-of-heat-sinks-and-their-importance/


 Chia sẻ:
Chia sẻ: